Cloud Security Pipeline
A fully automated pipeline that builds, tests, scans, and deploys applications securely. It runs unit tests, code and container scans, and infrastructure checks during every deployment, automatically blocking anything unsafe. Built with Python, Terraform, Docker, GitHub Actions, and AWS for safe, cost-free testing.
A hands-on DevSecOps simulation that builds, scans, and deploys a cloud application securely from code to cloud, all fully automated.
Technical Explanation
GitHub Actions runs pytest, Bandit, and Trivy before Terraform provisions infrastructure on AWS or LocalStack. Secrets are retrieved securely from AWS Secrets Manager, and all activity is logged through CloudTrail and GuardDuty.
Problem
In many organizations, code gets deployed without consistent security or quality checks. Manual testing and scanning are often skipped due to time pressure, leading to vulnerabilities in production.
Technical Explanation
This pipeline removes that risk by integrating security validation directly into the CI/CD process. Each code push triggers automated tests, scans, and infrastructure validation, enforcing security gates before deployment to AWS.
Approach
- Built a Python Flask web application packaged inside a Docker container for consistent deployment across environments.
- Defined AWS infrastructure using Terraform, creating EC2, S3, IAM with least privilege, Security Groups, Secrets Manager, CloudTrail, and GuardDuty.
- Configured GitHub Actions workflows to automatically run:
- pytest for functional and integration testing
- Bandit for Python code vulnerability scanning
- Trivy for Docker image scanning
- Deployment is blocked if any scan or test fails.
- Generated JSON reports stored in the
reportsfolder for audit purposes. - Added a custom Python port tester to verify that only approved ports 22 and 5000 remain open after deployment.
- Integrated AWS Secrets Manager for secure secret handling at runtime.
- Enabled LocalStack to simulate the full AWS environment locally to avoid billing costs.
Technical Explanation
GitHub Actions YAML workflows orchestrate testing and scanning in sequence, then deploy using Terraform commands. Boto3 manages secret retrieval from AWS Secrets Manager. Terraform automates EC2 provisioning and network setup. The port tester Python script validates network security after deployment.
Workflow Story: From Commit to Protection
The pipeline moves a change through clear gates. These snapshots walk through a typical run, showing how unsafe changes get stopped early and safe changes proceed.
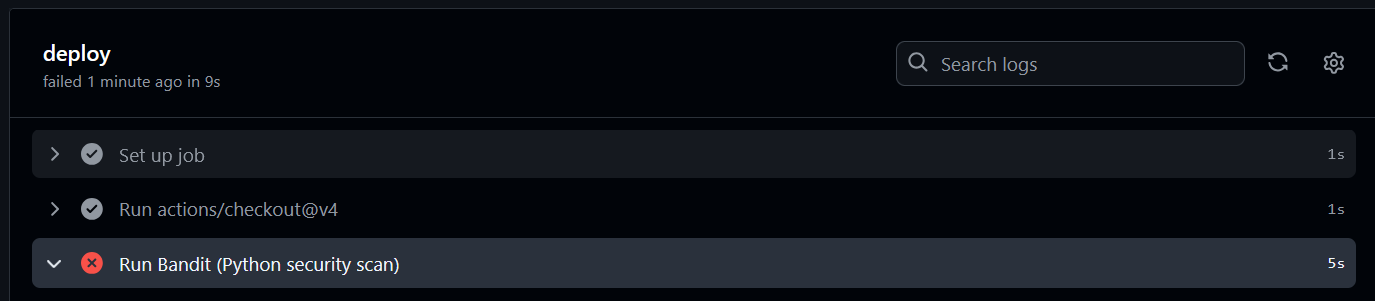
1) Push triggers security gates
On every push to main, GitHub Actions starts the deploy job. If a gate fails, the job halts and nothing is deployed.
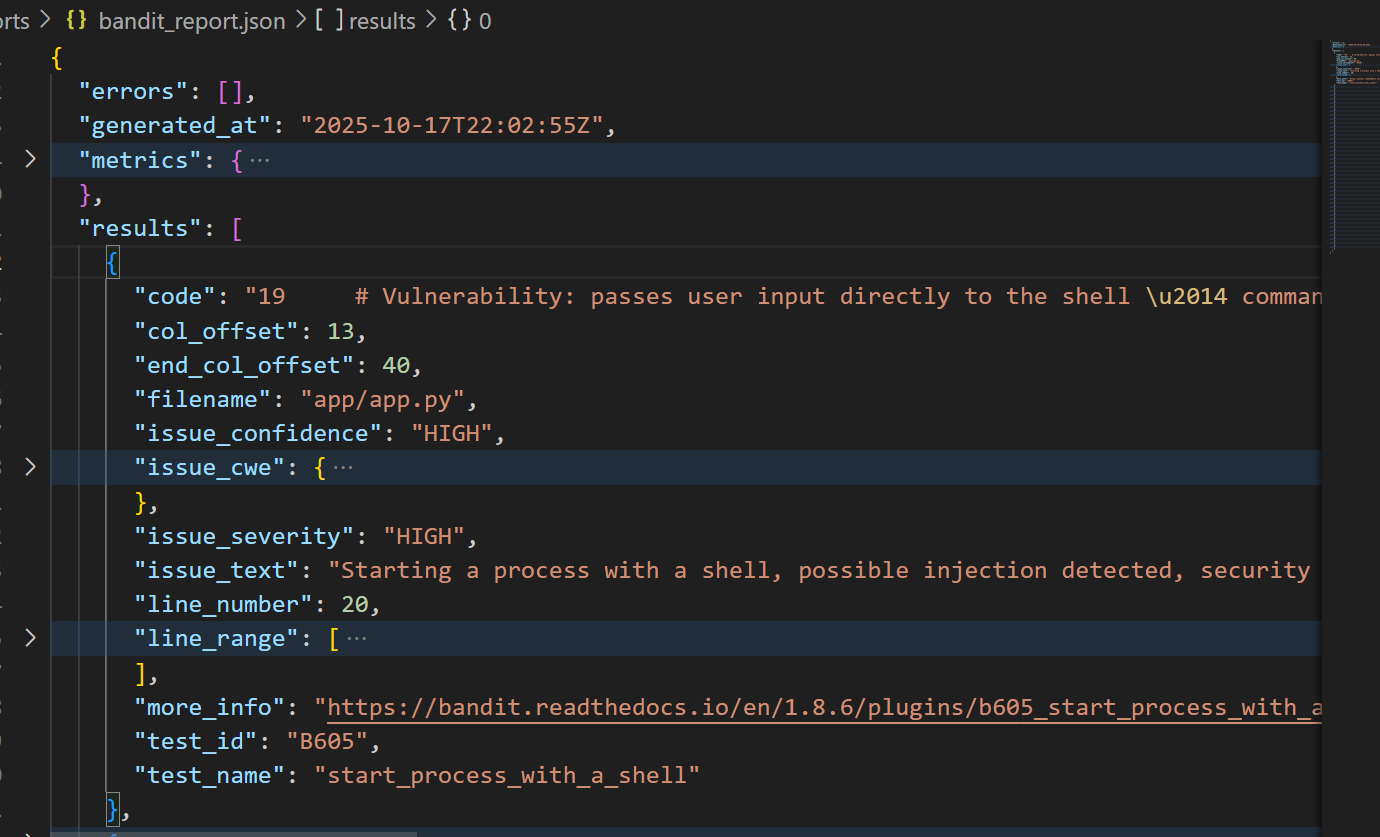
2) Bandit pinpoints risky code
Static analysis finds issues like starting a shell with user input (B605). The report includes file, line, CWE, and severity.
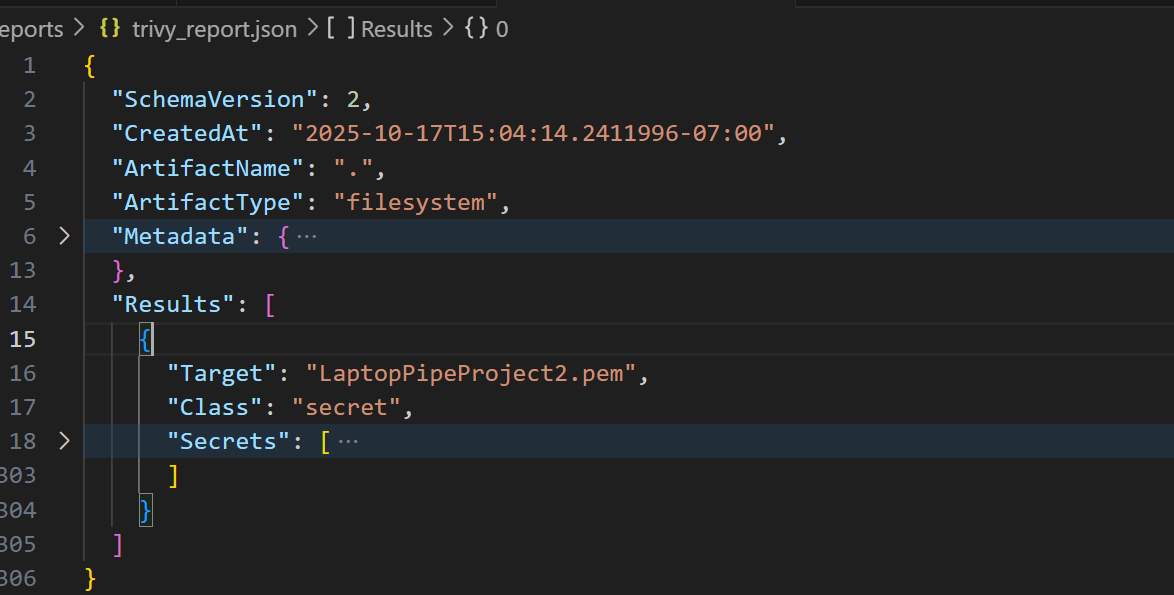
3) Trivy catches secrets and image issues
Trivy scans the repository and container images. Secret exposures or critical CVEs fail the run.
4) Preview infra with Terraform plan
After issues are fixed and scans pass, the job generates a Terraform plan so reviewers can see the exact infrastructure delta.

5) Preserve evidence for audits
Reports and logs are saved for reproducibility and compliance.
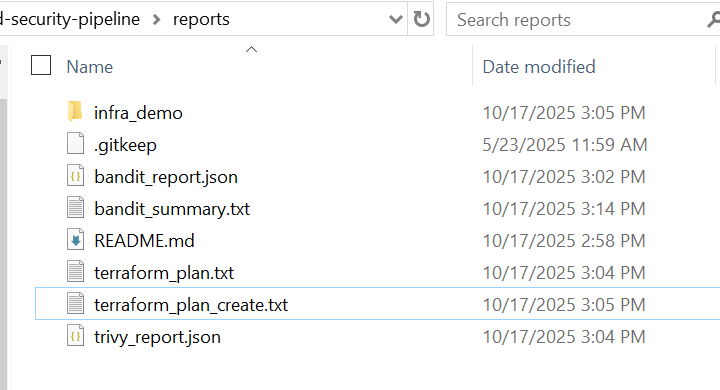
reports/.6) Green build after remediation
When all gates pass and the plan is approved, deployment finishes cleanly.
Results
- Every build is tested, scanned, and verified before deployment.
- Vulnerable images, insecure IAM roles, or open ports are automatically rejected.
- Detailed audit reports are produced for Bandit, Trivy, pytest, and Terraform validation.
- GuardDuty and CloudTrail continuously monitor and log activity for post-deployment visibility.
- Every CI/CD run is traceable in GitHub Actions with time‑stamped logs and security artifacts for audit and compliance review.
- Achieved fully automated, zero‑touch deployment from code to cloud with enforced security gates.
Technical Explanation
CI/CD results and logs are archived in the reports folder. Bandit and Trivy outputs are stored as JSON artifacts. Terraform state files and logs enable reproducible environments, while AWS GuardDuty provides runtime threat detection and continuous monitoring.
Tech Stack
- Languages: Python (Flask)
- Infrastructure: Terraform, AWS EC2, S3, IAM, Security Groups, Secrets Manager, CloudTrail, GuardDuty, LocalStack
- CI/CD and Security: GitHub Actions, Docker, pytest, Bandit, Trivy
- Automation and Scripts: Python (Boto3 and port tester), Bash
- Reports: JSON and log outputs stored in the
reportsfolder for audit and demo purposes
Technical Explanation
Each tool contributes to a distinct DevSecOps layer. Terraform provides infrastructure as code for AWS automation. Docker ensures consistent application packaging. GitHub Actions manages CI/CD and automated security workflows. Bandit and Trivy perform vulnerability scanning for code and containers. AWS services handle secret storage, logging, and threat monitoring. pytest verifies app stability through automated testing.